Carbon Impacts of CLT
Project Lead
Alison Kwok
Student Researchers:
Isabel Rivera
Hannah Zalusky
Hannah McKay
Advisor:
Lindsay Rasmussen, Architecture 2030
Project Duration
2018-2019
Facilities:
NetZED Laboratory – University of Oregon
Individual Builing Case Studies
Abstract
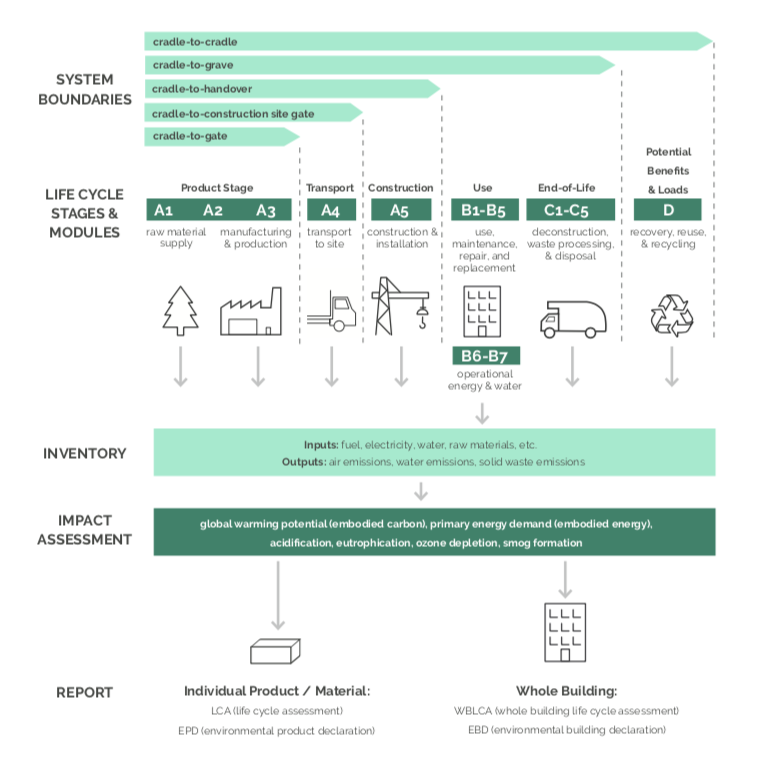
Whole building life cycle analysis (WBLCA) refers to a method to quantify and evaluate the environmental impacts associated with a building’s life cycle. This series highlights five whole building life cycle assessments of buildings incorporating the building material known as cross-laminated timber (CLT) into some or all of their structure, using a primary cradle-to-grave system boundary. The case study report will serve as an educational resource for academics, professionals, and CLT project stakeholders. While there is some uncertainty about the best way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from architecture and construction, using CLT and other wood building materials is one possible means to reduce the emissions associated with a building’s materials.
Introduction
CLT offers the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using timber, which requires much less energy to produce than steel or concrete and naturally sequesters carbon through its lifetime. However, there is a gap in the literature and a lack of general understanding about how much carbon CLT sequesters compared to the carbon emitted in the manufacturing process and in creating the adhesives used, as well as how the carbon value is calculated. This project analyzes and summarizes relevant literature and will create six case studies to illustrate the embodied carbon impacts of various kinds of mass timber buildings. In doing so, it aims to reduce confusion in the sector and assist designers and developers in making informed decisions regarding future green buildings.
Research Details
This research project had several components:
1) An info sheet series about CLT, focused on its environmental impacts
2) A case study series of whole building life cycle assessments for five buildings utilizing CLT
3) An annotated bibliography of significant sources for the info sheet and case study series

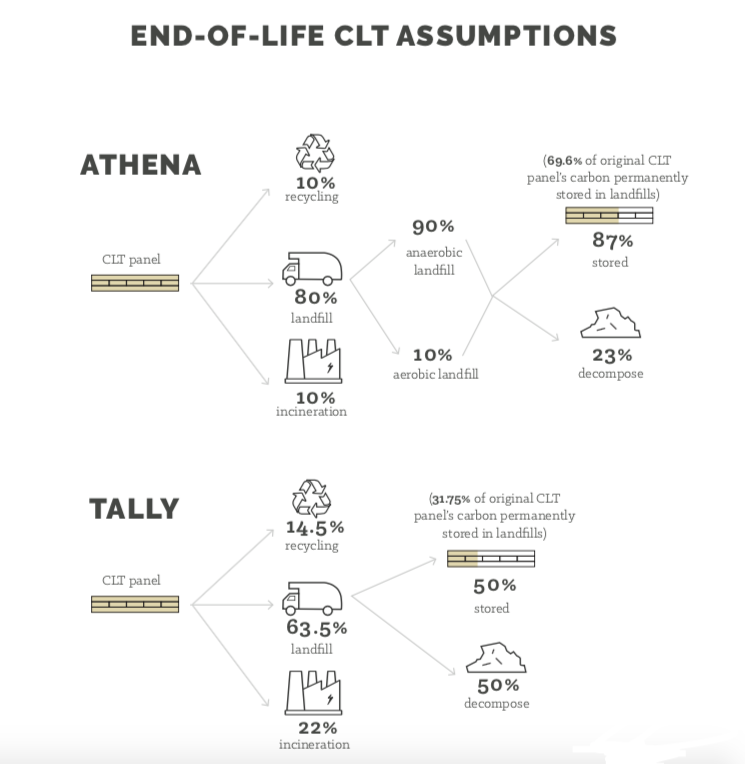
For the case study series, five firms generously provided digital documentation on one of their buildings, each of which used CLT in a prominent structural role. From the specifications and the digital model’s material quantities, the research team performed life cycle assessments in Tally and Athena Impact Estimator, two life cycle assessment software. Both software reports each building materials’ environmental impacts across several impact categories: global warming potential, acidification potential, eutrophication potential, smog formation potential, and primary energy demands. Due to differing methodologies and databases, the estimated environmental impacts often varied quite dramatically between the software. In some cases, Tally reported larger harmful impacts, while in other cases, Athena IE reported larger harmful impacts. For global warming potential, the value was heavily swayed by biogenic carbon methodologies and the inclusion or exclusion of module D.
The embodied carbon of buildings is typically measured by global warming potential and some biogenic carbon methodologies result in significantly lower estimations of global warming potential. Although LCA standards offer some guidance about biogenic carbon methodologies, there is still work needed to standardize end-of-life scenarios and assumptions about sustainable forestry. For CLT and other mass timber buildings, a consistent environmental assessment will help validate their potential environmental benefits.

Results:
MASS TIMBER LCA CASE STUDIES:
CLT BUILDINGS: A WBLCA CASE STUDY SERIES
Whole building life cycle analysis (WBLCA) refers to a method to quantify and evaluate the environmental impacts associated with a building’s life cycle. In this series, five buildings that incorporated cross-laminated timber (CLT) into their structures were assessed. These include a single-family house, a multi-family residential building, a parking garage, an office building, and an industrial building.
A general overview of the use of CLT in buildings, including design information and synthesis of research on sequestered and stored carbon.
INDIVIDUAL BUILDING CASE STUDIES (POSTER PDF):
Mass Timber Parking Garage Structure
Mass Timber MultiFamily Residential Structure

